In 2023, Namibia conducted its long-awaited national population census, offering an insightful look into the country’s demographic trends and providing vital data for future planning. One of the most striking revelations from the census was the noticeable slowing of population growth, signaling important social, economic, and policy shifts. As the country moves towards a more stable growth trajectory, this data will influence Namibia’s approach to resource allocation, urban planning, healthcare, and education. In this article, we’ll explore what the 2023 census reveals about Namibia’s population dynamics, the causes behind this slowdown, and what it means for the future of the country.
Understanding the Population Growth Trend in Namibia
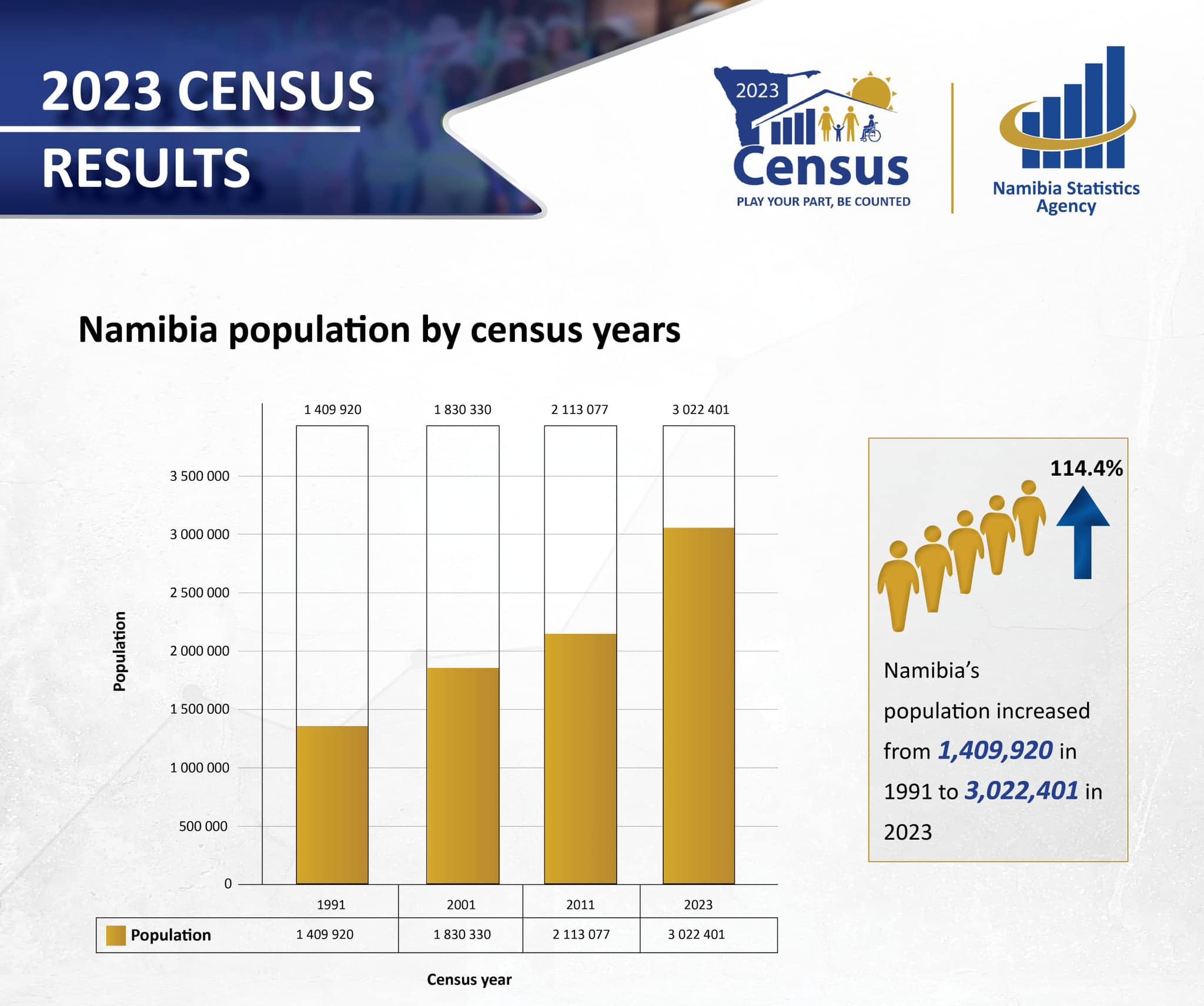
Namibia’s population growth has traditionally been on an upward trajectory since independence in 1990. However, according to the 2023 census, the rate of growth has markedly slowed in recent years. The census data, collected by the Namibia Statistics Agency (NSA), reveals that the annual population growth rate has dropped significantly when compared to previous decades.
In 1991, shortly after independence, Namibia’s population growth rate was around 3.1% per year, and this rate remained relatively high through the 1990s and early 2000s. By 2023, however, the growth rate had slowed to just over 1% annually. This decline in the growth rate can be attributed to several key factors, including fertility rate changes, urban migration patterns, improved healthcare, and economic shifts.
Key Findings of the 2023 Census
The 2023 Namibia Census has provided crucial insights into the country’s evolving population dynamics:
- Population Size: Namibia’s total population reached approximately 2.7 million people in 2023, reflecting continued, albeit slower, growth since the 2011 census, when the population stood at 2.1 million.
- Urbanization: One of the most significant findings of the census was the ongoing trend of urban migration. More Namibians are moving from rural areas to urban centers in search of better opportunities, resulting in a steady rise in the population of cities like Windhoek, Swakopmund, and Walvis Bay. The capital city, Windhoek, remains the most populous urban area, with over 450,000 residents, accounting for nearly 20% of the nation’s total population.
- Age Structure: The census revealed a shift in Namibia’s age demographic. The median age of the population has increased slightly, reflecting the nation’s aging population. The youth bulge that characterized Namibia’s demographics in the past decades is beginning to stabilize, though the youth still represent a significant proportion of the population, with nearly 60% under the age of 30.
- Gender Distribution: The gender ratio in Namibia remains relatively balanced, with slightly more women than men. Women make up about 51% of the total population, reflecting broader regional and global trends in gender disparities.
- Fertility Rates: A notable shift in Namibia’s demographic landscape is the declining fertility rate. Over the past few decades, Namibia’s fertility rate has fallen from about 5 children per woman in the early 1990s to around 3 children per woman by 2023. This decrease reflects broader societal changes, including improved access to contraception, higher education levels, and changing attitudes toward family planning.
Factors Behind the Slowdown in Population Growth
Several interconnected factors have contributed to the slowdown in Namibia’s population growth:
1. Fertility Rate Decline
The most significant factor in the slowing population growth is the decline in fertility rates. As women gain greater access to education, employment, and healthcare, they are choosing to have fewer children. Increased awareness of family planning methods, coupled with government initiatives and campaigns aimed at reducing child mortality, has allowed Namibians to make informed decisions about family size.
2. Improved Health and Life Expectancy
Namibia has made significant strides in improving healthcare and combating diseases like HIV/AIDS, which has historically been a major health challenge for the country. As a result, life expectancy has steadily increased, and infant mortality has decreased. The 2023 census indicated a continued improvement in life expectancy, which now stands at approximately 65 years for women and 60 years for men. As more people live longer, the overall growth rate slows as fewer young people are born in comparison to older generations.
3. Urbanization and Migration
Namibia’s continued urbanization plays a crucial role in the slower growth rate. Rural-to-urban migration is a trend that is shaping much of Namibia’s demographic future. Many young people are moving to urban areas for better educational and employment opportunities. This migration has led to population concentration in cities like Windhoek, Swakopmund, and Walvis Bay, while many rural areas, particularly in the northern regions, have experienced slower population growth or even population declines.
4. Economic Factors
Namibia’s economic performance also plays a role in demographic trends. The economic slowdown, particularly in recent years, has impacted population growth. Economic stagnation or contraction can deter young people from starting families, as job insecurity and a lack of financial resources affect their decisions on marriage and childbearing. Furthermore, Namibia’s relatively high unemployment rate, which hovers around 30%, especially among young people, has contributed to a decrease in birth rates.
5. Government Policies and Family Planning
The Namibian government has made significant investments in family planning, health education, and access to contraception. These measures have helped families make informed decisions and allowed women to pursue educational and career opportunities without the pressure of having large families. The Ministry of Health and Social Services has implemented nationwide campaigns promoting reproductive health and family planning, contributing to the continued decline in fertility rates.
The Impact of Slowing Population Growth on Namibia
The slowing of Namibia’s population growth has wide-ranging implications for the country’s future development. While the decline in growth presents challenges, it also opens up opportunities for addressing social, economic, and environmental concerns.
1. Resource Allocation and Planning
With slower population growth, Namibia can more effectively plan for future infrastructure development, education, and healthcare needs. The government will need to prioritize investment in urban development to accommodate the growing urban population while also ensuring that rural areas are not left behind.
2. Aging Population
An aging population presents challenges in terms of social services and healthcare. The Namibian government will need to plan for an aging population by developing policies that focus on elderly care, pension systems, and healthcare services tailored to the needs of older citizens.
3. Economic Development
Namibia’s economic future will rely heavily on harnessing the potential of its younger population. While the youth population is still relatively large, the country will need to focus on creating employment opportunities, improving skills development, and fostering entrepreneurship to ensure that young people have a chance to contribute meaningfully to the country’s economy.
4. Environmental Sustainability
The slowing population growth also provides Namibia with an opportunity to manage its natural resources more sustainably. With fewer people consuming resources, there may be greater potential for managing Namibia’s biodiversity, water resources, and energy use. The country can prioritize sustainable development initiatives to ensure that future generations can continue to thrive in its harsh, yet beautiful, environment.
The 2023 Census has provided Namibia with a clearer understanding of its population dynamics and demographic trends. The slowing of population growth signals a new chapter in Namibia’s development, where economic stability, healthcare improvements, and urbanization will shape the future. While challenges such as an aging population and rising urbanization need to be addressed, Namibia’s commitment to sustainable growth and social equity will allow the country to harness its demographic changes as an opportunity for progress. As Namibia continues to grow and evolve, its ability to adapt to these changes will define the country’s success in the coming decades.