Namibia, a stunning country located in the southwest of Africa, has long been a focal point for both researchers and travelers. With its vast deserts, rugged mountains, diverse cultures, and unique wildlife, Namibia is a nation of contrasts. One of the most important tools used to understand the country’s population dynamics, development, and future trends is its national census. The 2023 census, which provides a snapshot of Namibia’s population and key demographic indicators, offers a wealth of information that paints a detailed picture of the country’s present situation and its trajectory.
This article explores the key statistics from Namibia’s 2023 census, shedding light on the country’s population, fertility trends, urbanization, education levels, and more.
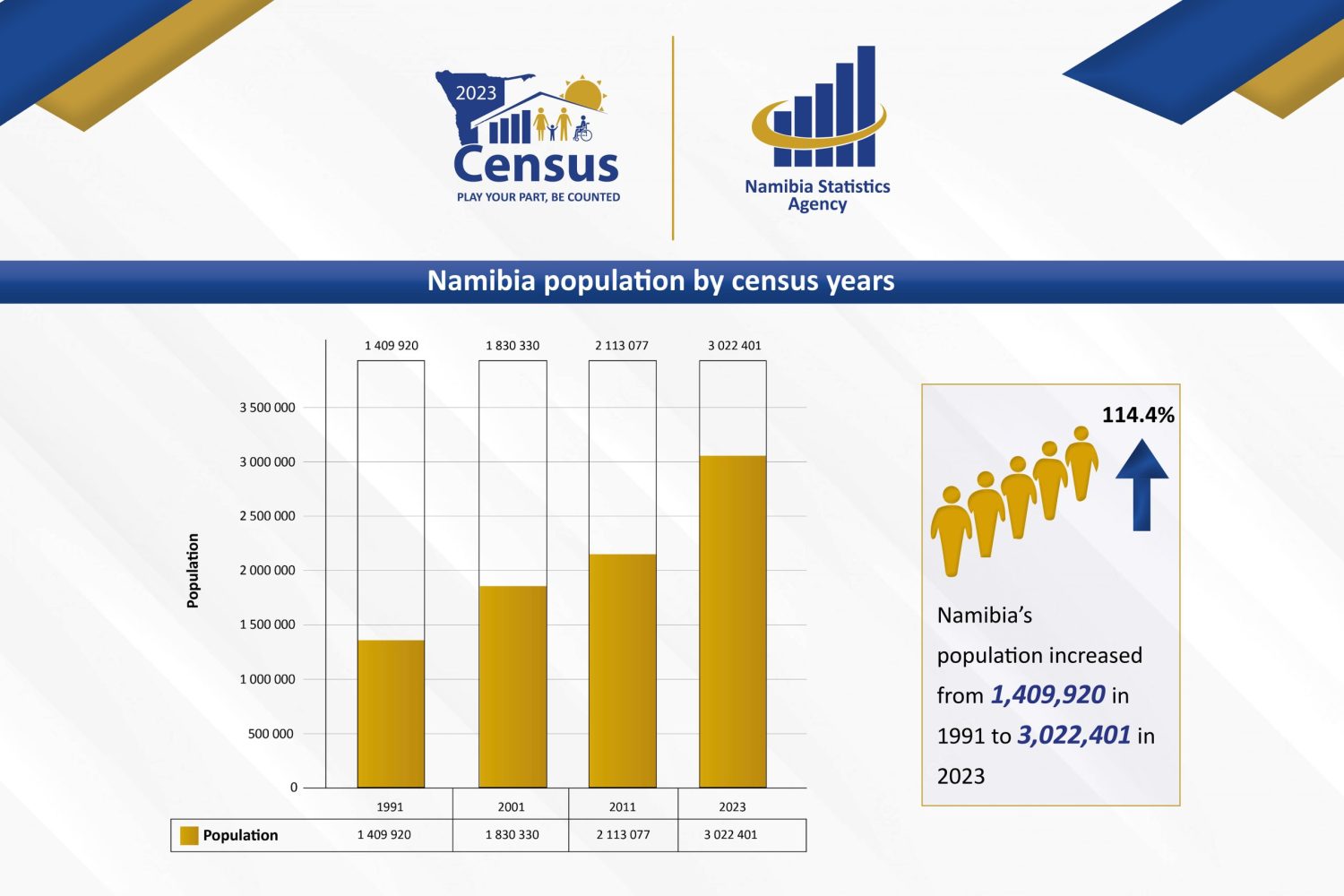
1. Namibia’s Population Growth: How Many People Live in Namibia?
As of the 2023 census, Namibia’s population stands at approximately 2.7 million people. This reflects a steady growth rate of about 1.82% per year, indicating a moderate increase in the country’s total population over the past decade. The growth rate, however, has slowed when compared to previous decades, a trend that can be attributed to decreasing fertility rates, migration patterns, and improvements in life expectancy.
Key Insights on Population:
- Total Population: 2.7 million people
- Growth Rate: 1.82% per year
- Population Density: Namibia remains one of the least densely populated countries in the world, with just over 3 people per square kilometer.
2. Fertility Rate and Population Structure: The Changing Family Landscape
One of the most significant demographic trends revealed by the 2023 census is the decline in Namibia’s fertility rate. The total fertility rate (TFR) stands at 2.7 children per woman, which is a significant decrease from 5.0 children per woman in the 1990s. This decline is in line with global trends and reflects changes in societal attitudes, greater access to family planning, and improvements in women’s education and employment opportunities.
- Total Fertility Rate (TFR): 2.7 children per woman
- Median Age: The median age of Namibia’s population is now around 20 years, signaling a relatively youthful population.
The decreasing fertility rate is a major factor in slowing population growth, and it also has implications for future economic development, including labor force participation and pension systems.
3. Urbanization: The Rise of Namibia’s Cities
Namibia is experiencing significant urbanization. The 2023 census reveals that approximately 54% of the population now resides in urban areas, with the remaining 46% living in rural regions. This marks a substantial increase in urbanization from previous decades, driven by internal migration as people move from rural areas in search of better economic opportunities, education, and healthcare.
Key Urbanization Stats:
- Urban Population: 54% of the total population
- Largest Cities: Windhoek, the capital, is the largest city in Namibia, followed by Swakopmund, Walvis Bay, and Rundu.
As Namibia’s cities grow, they face increasing pressure on infrastructure, housing, healthcare, and other urban services. Managing urban growth in a sustainable way will be a key challenge for policymakers in the coming years.
4. Age Distribution: A Youthful Population Facing an Aging Trend
While Namibia is still home to a young population, the 2023 census reveals a steady increase in the number of elderly citizens. The median age has risen, indicating that people are living longer due to improved healthcare. Namibia’s life expectancy is now 64 years, a significant improvement from the past, and this has contributed to a growing elderly population.
Age Distribution Insights:
- Proportion of Population Aged 60 and Above: Approximately 8% of Namibia’s population is 60 years or older, a figure that has been rising steadily.
- Youth Population: Around 42% of the population is under the age of 15, highlighting the continued youthfulness of the country.
The aging population presents a challenge for Namibia’s healthcare and pension systems, which will need to adapt to the needs of an older generation. At the same time, Namibia’s large youth population presents both opportunities and challenges in terms of employment, education, and social services.
5. Literacy and Education: Advancements in Human Capital
One of the most positive outcomes revealed by the 2023 census is the improvement in Namibia’s literacy rates. With 91.5% of the population aged 15 and above being literate, Namibia continues to make significant strides in education. This is reflective of the country’s ongoing investment in its education system, particularly in terms of access to primary and secondary education.
Key Education Stats:
- Literacy Rate: 91.5% of individuals aged 15 and above are literate.
- School Enrollment: Enrollment rates in primary and secondary education are high, although challenges remain in terms of access to tertiary education, especially for rural populations.
- Gender Equality: Gender parity in education has significantly improved, with girls and boys now having similar enrollment rates in schools.
However, while progress has been made, Namibia still faces challenges in terms of quality education and access to higher education, particularly in remote and rural areas. Addressing these disparities will be critical in ensuring that the country can fully capitalize on its human capital potential.
6. Employment and Unemployment: A Closer Look at the Job Market
Unemployment remains a significant challenge for Namibia, particularly among its youth. According to the census data, Namibia’s unemployment rate stands at approximately 34%, with youth unemployment being the most pressing issue. The country faces a mismatch between the skills of job seekers and the demands of the job market, leading to high levels of underemployment.
Key Employment Stats:
- Overall Unemployment Rate: 34% of the labor force is unemployed.
- Youth Unemployment: A large percentage of unemployed individuals are between the ages of 15 and 24, with rates often exceeding 50%.
- Underemployment: A significant portion of the employed population works in informal sectors or part-time jobs, often with little job security or benefits.
Addressing the unemployment challenge will require greater investment in skills development, vocational training, and creating more jobs, particularly in sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and services.
7. Gender: Progress and Challenges
Gender equality in Namibia has improved over the years, with women making significant strides in education, healthcare, and political representation. The 2023 census reveals that women now make up 52% of the population, and their participation in the workforce and public life is growing.
Key Gender Stats:
- Female Population: Women constitute 52% of Namibia’s total population.
- Labor Force Participation: While women are increasingly entering the workforce, gender disparities persist in employment opportunities and income levels.
- Political Representation: Namibia has one of the highest percentages of female politicians in Africa, with women holding key positions in government.
Despite these advancements, gender inequality remains a challenge, particularly in rural areas. Women still face higher rates of poverty and violence and have limited access to economic opportunities compared to men. Ensuring gender equality in all spheres of life will be vital for Namibia’s future development.
8. Health and Life Expectancy: Achievements and Ongoing Challenges
Life expectancy in Namibia has steadily improved over the years, rising to 64 years for both men and women, according to the census. This increase is largely due to better access to healthcare, improvements in sanitation, and the reduction in HIV/AIDS-related deaths due to effective antiretroviral treatments.
Health Insights:
- Life Expectancy: 64 years for both men and women.
- HIV/AIDS: While Namibia has made significant progress in combating HIV/AIDS, the epidemic remains a critical health challenge, particularly in rural areas.
- Infant Mortality: The infant mortality rate has also decreased significantly, reflecting improvements in maternal and child healthcare.
Although health indicators have improved, Namibia still faces challenges in terms of healthcare accessibility, particularly for rural and remote populations. Strengthening the healthcare system will be essential to further improve health outcomes.
9. Migration Trends: Internal and External Movement
Migration, both within Namibia and from neighboring countries, continues to shape the demographic landscape. Internal migration from rural areas to urban centers has been a significant driver of population growth in cities, while external migration from countries like Angola and Zambia has also contributed to population changes.
Key Migration Stats:
- Internal Migration: 46% of the population still resides in rural areas, though urban migration is increasing.
- External Migration: Namibia has seen steady migration flows, particularly in the context of regional employment opportunities and economic conditions.
Migration trends will continue to influence population distribution, urban planning, and economic development.
The 2023 census has provided a comprehensive and valuable snapshot of Namibia’s demographic trends. With a population of 2.7 million people, the country is experiencing key shifts, including declining fertility rates, increasing urbanization, an aging population, and improving literacy rates. These trends present both challenges and opportunities for the nation, particularly in terms of labor market dynamics, social services, and infrastructure development.
Namibia’s ability to adapt to these demographic changes will be crucial in ensuring sustainable economic growth and improving the well-being of its people. Addressing youth unemployment, managing urban growth, and improving gender equality and healthcare access will be key priorities in shaping the future of this beautiful and diverse nation.
Join 'Namibia Today' WhatsApp Channel
Get the breaking news in Namibia — direct to your WhatsApp.
CLICK HERE TO JOIN