Namibia, a country rich in natural beauty and cultural heritage, is home to one of the most fascinating and ancient forms of art—rock art. These timeless depictions etched into the walls of caves, cliffs, and rocks provide an invaluable window into the lives, beliefs, and practices of the indigenous peoples who once inhabited the land. From the striking depictions of animals to the symbolic representations of human figures, Namibia’s rock art offers a profound connection to the distant past, linking modern-day Namibians with their ancient ancestors.
In this article, we will delve into the significance of Namibia’s ancient rock art, the various styles and forms it takes, and how it has shaped our understanding of early human culture. We will also explore the efforts being made to preserve and protect these cultural treasures, which continue to capture the imagination of researchers and visitors alike.
1. The Significance of Namibia’s Rock Art
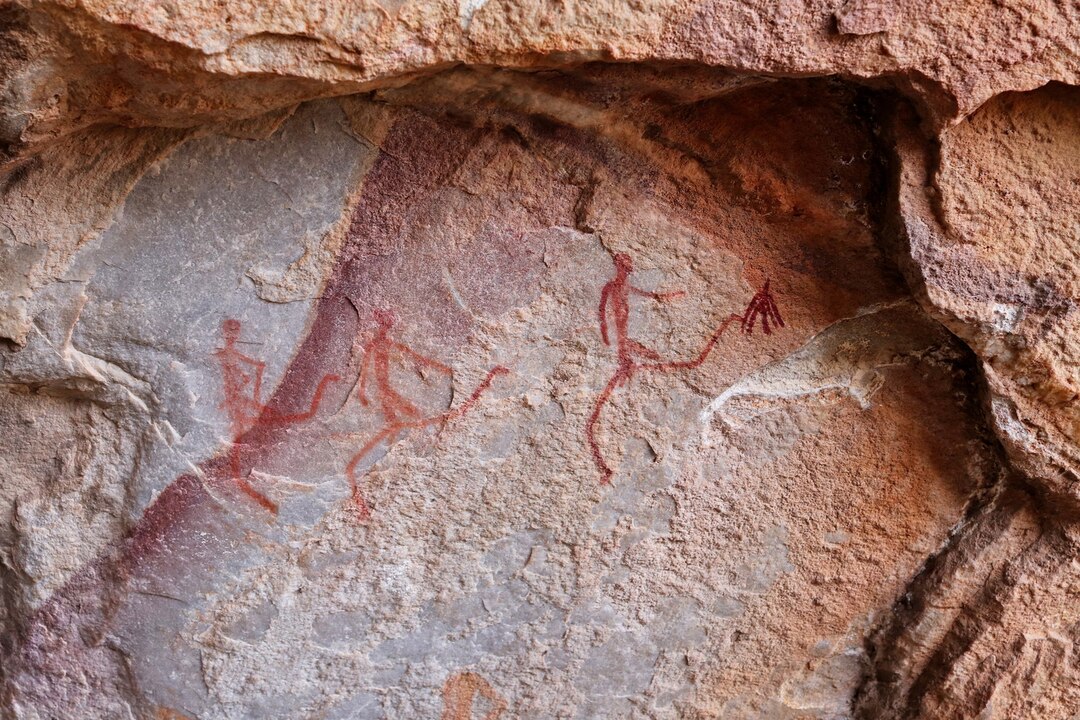
Namibia’s rock art is more than just a collection of ancient drawings—it is a cultural treasure that provides insights into the social, spiritual, and daily lives of the indigenous people. The rock art found across the country, particularly in the Damaraland and Brandberg Mountains, is believed to have been created over 5,000 years ago, making it some of the oldest rock art in the world. These images, often painted or engraved on rock surfaces, depict a wide range of subjects, including animals, humans, and abstract symbols, offering clues to the beliefs, rituals, and environmental conditions that influenced the early inhabitants of the region.
The rock art is primarily associated with the San (also known as Bushmen) and Khoikhoi peoples, two of the earliest inhabitants of Namibia. For centuries, these indigenous groups have used rock art as a means of storytelling, spiritual expression, and communication with the divine. These works of art are deeply intertwined with the oral traditions of the San people, who used the images to pass down knowledge about hunting, social norms, and the spiritual world.
2. Styles and Forms of Rock Art in Namibia
Namibia’s rock art comes in a variety of styles, each representing different time periods, cultures, and artistic techniques. Broadly, these styles can be categorized into two main groups: paintings and engravings.
Rock Paintings
The most iconic form of rock art in Namibia is the rock paintings, which are found in many of the country’s most significant archaeological sites. The paintings are typically done using natural pigments, such as ochre, charcoal, and clay, which were mixed with binders like animal fat or plant extracts to create paints. These pigments were applied to the rock surfaces with brushes made from twigs, animal hair, or fingers.
One of the most famous examples of rock paintings in Namibia is found in the Brandberg Mountain, home to the White Lady painting, which is thought to be one of the most important and enigmatic rock art sites in the country. The White Lady painting depicts a human figure surrounded by animals and is believed to have been created around 2,000 years ago. The symbolism of the figure is still debated, with some suggesting it represents a spiritual leader, while others propose it is a shamanistic or ritualistic depiction.
Another notable example is the Twyfelfontein site, a UNESCO World Heritage Site known for its rich collection of petroglyphs (rock engravings) and paintings. This site features images of animals, including elephants, giraffes, and lions, as well as geometric patterns and symbols. It is considered one of the most significant concentrations of rock art in Africa, with more than 2,500 individual carvings and paintings.
Rock Engravings
In addition to paintings, rock engravings are another prevalent form of ancient art in Namibia. Engraving involves the use of sharp tools, such as stone chisels or bones, to carve images into the rock surface. These images are often more intricate and detailed than the painted works, showcasing a range of animals, human figures, and symbolic motifs.
The Twyfelfontein rock engravings are particularly famous, with the site housing over 2,500 petroglyphs. The engravings often depict animals, such as antelopes and rhinos, as well as human figures engaged in hunting or dancing. Many of the engravings are thought to have been created by the San people, whose detailed knowledge of their environment is reflected in their art. The presence of animal tracks, spear symbols, and figures suggest that the engravings served as a record of hunting, migration, and ritualistic practices.
3. Symbolism and Interpretation
The rock art of Namibia is deeply symbolic, with each image carrying layers of meaning. While much of the art remains open to interpretation, it is widely believed that the images served several purposes:
- Spirituality and Shamanism: Many of the figures and symbols in the rock art are thought to represent spiritual beings, gods, or ancestral spirits. The San people are known for their deep connection to the spiritual world, and their rock art often reflects this relationship. Images of dancing, trance-like figures, and animals may be linked to shamanistic practices, where the shaman enters a trance to communicate with the spirit world.
- Hunting and Rituals: The depiction of animals, hunting scenes, and human figures suggests that rock art played a role in recording hunting practices and rituals. Some of the animals, such as the elephant and rhino, are considered sacred, and their portrayal in the art could signify their importance in the spiritual or ceremonial life of the people.
- Social and Cultural Identity: Rock art also served as a way to express social and cultural identity. The figures of human beings depicted in the art, often shown with exaggerated features or in ritualistic poses, may represent specific individuals or groups. The art likely functioned as a visual record of significant events, social structures, and cultural practices.
4. The Role of Rock Art in Understanding Human History
The study of Namibia’s rock art is crucial for understanding the broader history of humanity. The images provide researchers with a unique insight into the early human experience, particularly in relation to the development of communication, social organization, and belief systems.
By examining the rock art, anthropologists, archaeologists, and historians have been able to piece together elements of the lives of the indigenous peoples of Namibia. The images also offer valuable clues about the environment in which these people lived, shedding light on the flora and fauna of the region, as well as the changing climate over millennia.
For example, the paintings and engravings of animals provide evidence of species that were once abundant in Namibia but have since become extinct or migrated away. The depiction of large herbivores, such as giant eland and buffalo, shows that Namibia’s environment was once much wetter and more conducive to larger populations of animals.
5. Conservation and Protection of Namibia’s Rock Art
The preservation of Namibia’s rock art is an ongoing challenge, as these ancient treasures face threats from natural erosion, climate change, and human activity. With their delicate nature, rock paintings and engravings are susceptible to weathering, while increased tourism and vandalism pose additional risks.
The Namibian government, in collaboration with international organizations, has taken steps to protect and conserve these invaluable cultural artifacts. The National Heritage Council of Namibia has implemented several initiatives to safeguard rock art sites, including the establishment of protected areas and the development of visitor management strategies at major rock art sites like Twyfelfontein and Brandberg. Additionally, local communities are being encouraged to take an active role in the preservation of rock art by promoting awareness and responsible tourism.
Namibia’s ancient rock art offers a fascinating glimpse into the past, providing us with a deeper understanding of the lives and beliefs of the country’s early inhabitants. From the enigmatic White Lady painting to the intricate engravings of Twyfelfontein, Namibia’s rock art is not just an artistic achievement, but a profound connection to the country’s spiritual, cultural, and environmental history. As efforts continue to preserve and protect these ancient treasures, Namibia’s rock art will remain a testament to the ingenuity, creativity, and resilience of the indigenous peoples who once called this land home. Through ongoing research, conservation, and public education, Namibia’s rock art will continue to inspire awe and curiosity for generations to come.
Join 'Namibia Today' WhatsApp Channel
Get the breaking news in Namibia — direct to your WhatsApp.
CLICK HERE TO JOIN