Namibia, renowned for its stunning landscapes, vast deserts, and abundant wildlife, has become a prime destination for nature enthusiasts and wildlife conservationists. While the country’s national parks and reserves are well-known, private game reserves are also playing an increasingly significant role in boosting Namibia’s economy. These privately-owned reserves not only support conservation efforts but also create sustainable economic opportunities for local communities, contribute to Namibia’s tourism industry, and enhance the country’s overall financial growth.
In this article, we will explore how private game reserves in Namibia are impacting the economy and contributing to both environmental sustainability and social development.
The Role of Private Game Reserves in Namibia
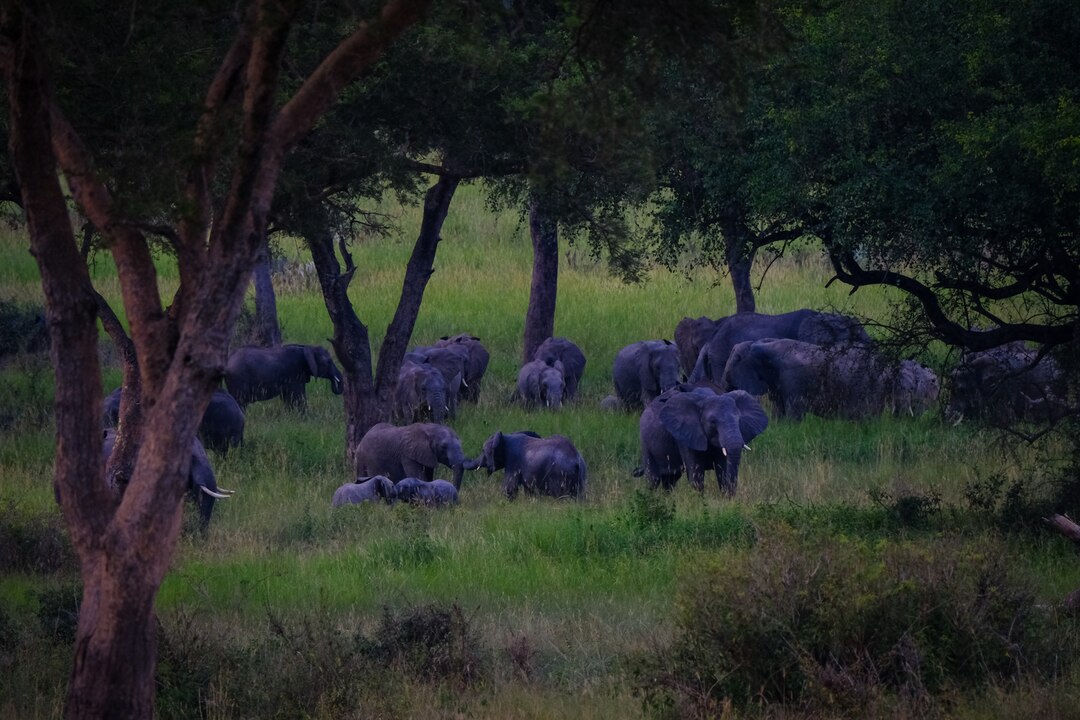
Private game reserves are large, privately-owned parcels of land that are designated for wildlife conservation and eco-tourism. These reserves are typically managed by private individuals, conservation organizations, or companies, and they are often located in some of Namibia’s most beautiful and ecologically significant areas. While national parks such as Etosha National Park draw large numbers of visitors, private game reserves offer a more exclusive, intimate experience, attracting eco-conscious tourists from around the world.
Economic Impact of Private Game Reserves
The economic benefits of private game reserves in Namibia are multifaceted, affecting various sectors such as tourism, employment, conservation, and infrastructure development. These reserves play a key role in generating revenue, creating jobs, and driving local development. Below are the primary ways private game reserves contribute to Namibia’s economy:
1. Tourism Revenue
Tourism is one of Namibia’s largest economic contributors, and private game reserves play a crucial role in attracting both domestic and international visitors. Visitors to these reserves pay for various services such as entrance fees, guided tours, accommodation, and wildlife activities like game drives, birdwatching, and nature walks.
According to Namibia’s Ministry of Environment, Forestry, and Tourism, eco-tourism and wildlife-related tourism contribute millions of Namibian dollars to the country’s GDP. Private reserves like Phinda Game Reserve, Damaraland and Kulala Wilderness Reserve have positioned themselves as premium eco-tourism destinations, attracting high-spending tourists who seek luxury accommodations, exclusive safari experiences, and the chance to see rare wildlife.
Increased tourism revenues have a direct positive impact on Namibia’s economy, boosting foreign exchange earnings and supporting the hospitality and transport sectors. Private game reserves, through partnerships with tour operators and international travel agencies, help market Namibia as a luxury travel destination, attracting tourists who would not have visited the country otherwise.
2. Job Creation and Community Development
Private game reserves create thousands of jobs across various sectors. These jobs range from park rangers, guides, chefs, housekeepers, and administrative staff to marketing professionals, security personnel, and hospitality workers. Employment in private reserves is especially vital in rural areas where other job opportunities may be limited.
Additionally, many private game reserves are committed to hiring local people from nearby communities, thereby ensuring that the benefits of tourism trickle down to those who need it most. Many reserves run training programs to equip local residents with skills in hospitality, tourism, and wildlife conservation, which helps build a skilled workforce and offers long-term career opportunities.
The growth of private game reserves has also led to improved infrastructure, such as better roads, transportation systems, and healthcare facilities, which directly benefit the local communities. Many reserves provide financial support for local schools, clinics, and community projects, enhancing the quality of life for nearby residents.
3. Conservation Funding and Environmental Protection
Private game reserves are key players in Namibia’s conservation efforts. Unlike traditional government-run parks, these reserves are funded entirely by private individuals or organizations, allowing for more flexibility in management and long-term sustainability. Private game reserves often focus on protecting endangered species and restoring ecosystems, contributing to the preservation of Namibia’s rich biodiversity.
Revenue generated from tourism is often reinvested in conservation initiatives such as habitat restoration, anti-poaching programs, wildlife monitoring, and sustainable land management practices. This approach helps safeguard the country’s wildlife and natural landscapes, providing essential resources for ongoing conservation efforts.
For example, Namibia has become a leader in community-based conservation, where private game reserves work alongside local communities to protect wildlife and natural habitats. The Namibian conservancy model involves giving communities the legal rights to manage and benefit from wildlife on their land, with private reserves playing an important role in supporting this model through partnerships.
4. Sustainable Agriculture and Land Management
In addition to promoting wildlife conservation, private game reserves also contribute to sustainable land management and agriculture. Many reserves incorporate wildlife-friendly farming and grazing practices that minimize the impact of livestock farming on the environment. For instance, some private reserves have integrated agro-tourism initiatives, where visitors learn about sustainable farming and land restoration techniques.
Moreover, private game reserves that focus on ecotourism often adopt sustainable building practices, water conservation measures, and renewable energy sources, all of which contribute to the country’s goal of sustainable development.
5. Promotion of Namibia’s Global Image
As Namibia’s private game reserves gain international recognition, the country’s image as a global leader in eco-tourism is being strengthened. High-profile reserves such as Wolwedans, Mowani Mountain Camp, and Omajova Private Reserve are becoming increasingly popular among tourists seeking luxury safaris that emphasize both conservation and responsible tourism.
The promotion of Namibia as a prime destination for eco-tourism through private game reserves enhances the country’s global profile. This, in turn, leads to greater investment from international tour operators, eco-tourism developers, and conservation organizations. By showcasing Namibia’s commitment to preserving its natural beauty and wildlife, private game reserves are helping the country establish itself as a leader in sustainable tourism.
The Challenges and Opportunities for Private Game Reserves in Namibia
While private game reserves play a significant role in boosting Namibia’s economy, they also face challenges, particularly in terms of maintaining profitability and sustainability. Some of the key challenges include:
1. Climate Change
Namibia’s arid climate means that its ecosystems are particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Droughts, unpredictable rainfall, and changing temperatures can impact wildlife populations and the overall health of private game reserves. To mitigate these challenges, private reserves need to invest in climate adaptation strategies and water conservation measures.
2. Increased Competition
With the growing popularity of Namibia as an eco-tourism destination, private game reserves are facing increased competition from other wildlife destinations in Africa. To remain competitive, reserves must continue to innovate and offer unique experiences to attract tourists.
3. Sustainable Development
While private game reserves contribute to conservation and sustainable tourism, the pressure to balance profitability with environmental responsibility remains a challenge. Implementing sustainable practices across all aspects of operations—from tourism to land management—is essential for the long-term success of these reserves.
Private game reserves in Namibia are playing a transformative role in the country’s economy. Through the revenue generated from eco-tourism, the creation of jobs, the promotion of conservation, and the development of sustainable land management practices, these reserves contribute significantly to Namibia’s financial and environmental health. As the demand for eco-tourism continues to rise globally, Namibia’s private game reserves will remain a key driver in the country’s economic growth, ensuring a sustainable and prosperous future for its wildlife, landscapes, and communities.
By embracing the opportunities and overcoming the challenges, Namibia can continue to develop its private game reserves into a model of sustainable, profitable, and community-driven tourism that benefits both the local population and the natural environment. The economic and ecological contributions of these reserves are proving that conservation and tourism can work hand in hand to support a thriving and resilient economy.